 AC-type residual current devices The symbol is
AC-type residual current devices The symbol is 
This type of differential switch is sensitive only to alternating leakage currents. They were the first on the market and should be present in any domestic installation. They work correctly in installations that have practically no electronic components and are located in zones where storms are infrequent. However, if the house is located in a zone where there are frequent summer storms and atmospheric discharges (lightning) that cause power surges and earth leakages, or if its interior installation has several receptors with electronic components (smart electrical appliances, low-consumption or dimmable lighting, computer power supplies, air conditioning units, music player, television, etc.) where there could be pulsed direct current leakages (which can be as dangerous as alternate current but is not detected by AC residual current devices), residual current devices of this type are not suitable for installations with electronic components or in areas where there are frequent storms causing them to suddenly trip due to the distortion caused by these receptors. In fact, they are no longer permitted in some countries, like Germany and Switzerland.
 Differential class A. Their symbol is
Differential class A. Their symbol is 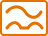
This type of differential switch is sensitive to alternating and continuous leakage currents and also includes a high-frequency filter which improves its magnetic core to prevent unexpected trips caused by harmonics generated when there are different receptors with electronic components. These features mean this type of differential switch is suitable for installations with receivers with electronic components.
 Superimmunised A-type differential switches. Their symbol is
Superimmunised A-type differential switches. Their symbol is  or
or 
This type of differential switch is the same as the A-type, but its trip curve approaches the limits set by Standard 61008-1, enabling it to function correctly in installations with strong loads of receptors with electronic components, such as electronic lighting reactances, variable speed drives, electronic igniters and where there is a large number of computers.
This type of differential switch also includes an energy accumulation circuit which significantly reduces sudden trips caused by occasional earth leakages associated with transient surges caused primarily by atmospheric discharges, differentiating them from a real defect. This means that this type of differential switch is sensitive to alternating and continuous leakage currents, greatly reducing sudden trips and making them more suitable for installations with receivers with electronic components or ones located in areas with frequent storms.
There are other types of differential switches, such as “Delayed” (S-type) for installations upstream of other differential switches; “Industrial” (B- and F-type) for recharging vehicles, engine ignitions and variable speed drives; and “Rearmable” for unattended installations that require a guarantee of continuity of service, although they are more generally used in industrial and commercial installations. But in domestic supplies, to maximise protection of people and prevent sudden trips, the conclusion is that:

